Last Updated on June 9, 2024 by Dan Campbell
When it comes to maintaining your equipment, choosing the right oil for your machines is crucial. Understanding the differences between SAE 30 and 10w-30 oil can significantly impact the performance and longevity of your engines. Whether you’re running a generator, a chainsaw, or a lawn mower, the right oil ensures smooth operation and reduces wear and tear. In general however, the choice between SAE 30 vs 10w-30 will come down to your locations temperature. For colder climates, 10w-30 is more practical, however SAE 30 can be more economical if you live in a warmer climate.
In this article, we will delve into the specifics of SAE 30 vs 10w-30 oil, providing you with a clear understanding of their properties, applications, benefits, and what differences there are between the two types.
Basics of SAE 30 & 10w-30 Oils
Oil is the lifeblood of any engine, providing lubrication, reducing friction, and helping to regulate temperature. Choosing the right oil ensures that your machinery operates smoothly, with fewer breakdowns and longer lifespan. Specifically, I’m talking about the using SAE 30 or 10w-30 oil since these are commonly used and can be confused.

SAE 30 oil is a single-grade oil, meaning its viscosity is stable and does not change significantly with temperature variations. It is commonly recommended for use in warmer climates and for older engines that are specifically designed for this type of oil. On the other hand, 10w-30 is a multi-grade oil, designed to perform well across a range of temperatures. The “10w” denotes its viscosity in colder temperatures, making it easier to start engines in winter, while the “30” indicates its performance at the engine’s operating temperature.
Understanding these differences is particularly important for how well your equipment functions in various weather conditions. Choosing the correct oil can mean the difference between smooth operation and frequent, costly repairs.
Moreover, the benefits of using the right oil extend beyond engine longevity. Efficiently running machinery consumes less fuel and reduces emissions. It also ensures that your tools and equipment are ready to perform when you need them the most, without unexpected downtime.
Key Terms and Concepts
To fully grasp the significance of choosing between SAE 30 and 10w-30 oil, it’s essential to understand some key terms and concepts related to engine oils. Here, I’ll define these terms and explain their relevance, ensuring you have a comprehensive understanding.
Viscosity: Viscosity is a measure of a fluid’s resistance to flow. In the context of engine oils, it indicates how thick or thin the oil is at certain temperatures. High viscosity means the oil is thicker and flows more slowly, while low viscosity means it’s thinner and flows more easily. Oil viscosity is crucial for engines because it directly impacts the lubrication performance, protection, and overall efficiency of the engine.
SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers) Ratings: The SAE rating is a standardized grading system that indicates the viscosity of engine oils. For example, SAE 30 is a single-grade oil with a consistent viscosity at operating temperature, while 10w-30 is a multi-grade oil that adjusts its viscosity for better performance in different temperatures.
Single-Grade Oil: Single-grade oils, like SAE 30, maintain a constant viscosity and are typically used in engines operating under consistent temperature conditions. They are simpler in formulation and generally preferred for older engines that were designed with single-grade oils in mind.
Multi-Grade Oil: Multi-grade oils, such as 10w-30, are formulated to provide adequate viscosity across a broader range of temperatures. The “10w” signifies the oil’s viscosity in cold conditions (the “w” stands for winter), making it easier to start an engine in lower temperatures. The “30” represents the oil’s viscosity at the engine’s operating temperature.
Oil Additives: Additives are chemicals added to oil to enhance its performance. They can include detergents to clean the engine, anti-wear agents to protect moving parts, and antioxidants to prevent oil degradation. Understanding the additives in your oil can help you choose the best product for your specific needs.
Synthetic vs. Conventional Oil: Synthetic oils are chemically engineered to provide superior performance and protection compared to conventional (mineral) oils. They offer better stability at extreme temperatures and longer intervals between oil changes. However, they are also more expensive. Conventional oils are derived from refined crude oil and are sufficient for many engines, especially older models or those used in mild conditions.
To visually see how cold weather can effect different oil weights, check out this video below of a few oil types cooled down to -40C and poured at the same time. The difference is quite apparent and pretty extreme!
By understanding these key terms and concepts, you’ll be better equipped to make informed decisions about the type of oil that best suits your needs. Whether you choose SAE 30 for its simplicity and stability in warm climates or 10w-30 for its versatility and cold-start performance, knowing the pros and cons will help you maintain your equipment effectively and ensure its longevity.
Key Differences Between SAE 30 and 10w-30
Before I get into details about each oil individually, let’s go over some of the key differences between the two types. Each type of oil has its own unique characteristics, making it suitable for different applications and operating conditions. Below, I’ve outline the major differences and their implications, helping you choose the right oil for your needs.
Viscosity and Temperature Adaptability
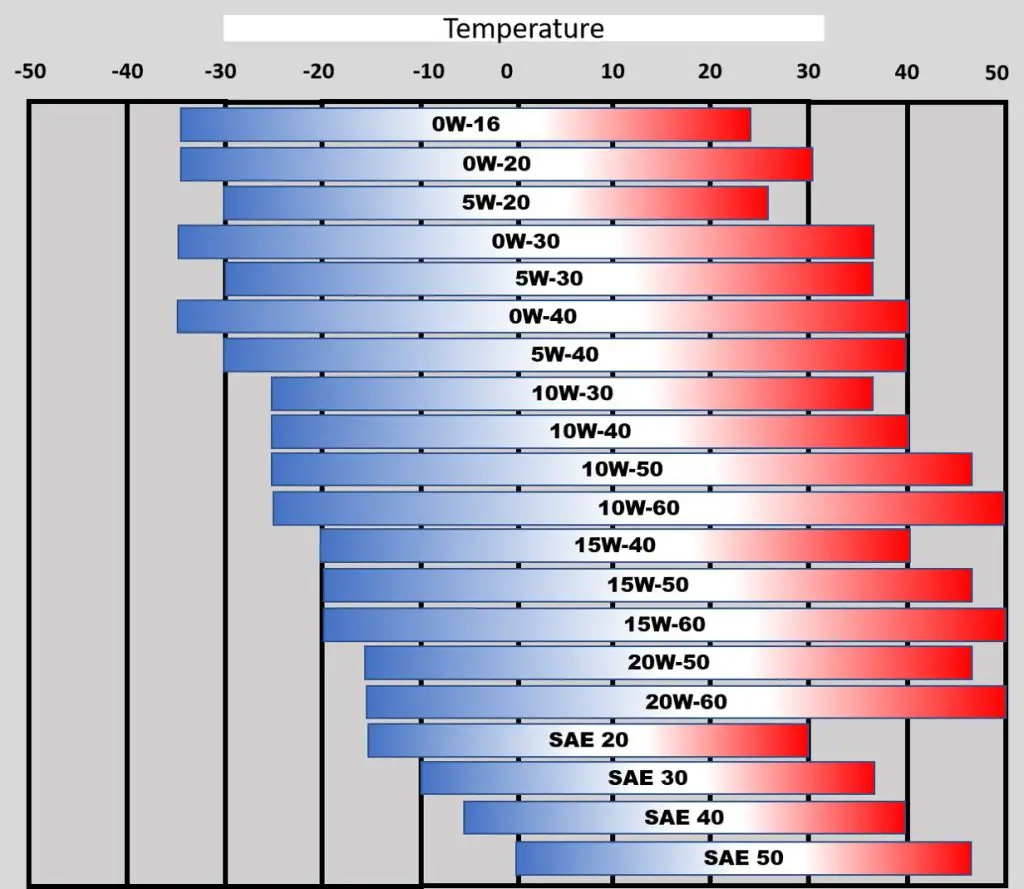
- SAE 30: This is a single-grade oil with a stable viscosity that remains consistent at operating temperatures (around 100°C or 212°F). It is not designed to handle significant temperature variations, making it ideal for use in warm climates or stable temperature conditions.
- Preferable Use Case: SAE 30 excels in older engines and equipment used in warmer environments. It’s commonly used in lawn mowers, small tractors, and other garden machinery where temperatures do not fluctuate significantly.
- Impact of Using Incorrectly: Using SAE 30 in cold conditions can lead to poor engine start-up, increased wear, and potential engine damage due to insufficient lubrication at low temperatures.
- 10w-30: This is a multi-grade oil designed to adapt its viscosity across a wide range of temperatures. The “10w” rating means it performs well in cold temperatures, while the “30” rating ensures proper viscosity at operating temperatures.
- Preferable Use Case: 10w-30 is versatile and suitable for engines operating in varying temperatures. It is ideal for generators, vehicles, and other equipment that must start reliably in both cold and warm conditions.
- Impact of Using Incorrectly: Using 10w-30 in older engines designed for single-grade oils can sometimes lead to compatibility issues. However, the broader risk is minimal compared to using SAE 30 in cold climates.
Seasonal and Environmental Considerations
- SAE 30:
- Excels In: Consistent, warm environments where the temperature stays relatively high. It is straightforward and often more economical, making it a good choice for equipment that doesn’t face extreme cold.
- Considerations: Ensure the ambient temperature is suitable for SAE 30 to avoid cold start issues. It’s particularly effective for summer use or in regions where winters are mild.
- 10w-30:
- Excels In: Environments with significant temperature changes. It provides reliable performance in both winter and summer, making it suitable for year-round use.
- Considerations: Its versatility makes it slightly more expensive, but the cost is offset by the convenience of not needing to change oil types seasonally. It’s also beneficial for modern engines designed to use multi-grade oils.
Potential Short-Term and Long-Term Effects
- Using SAE 30 in Cold Conditions:
- Short-Term: Difficult engine start-ups, increased engine wear.
- Long-Term: Potential for increased engine damage and reduced engine life due to inadequate lubrication during cold starts.
- Using 10w-30 in Warm Conditions:
- Short-Term: Generally no adverse effects, as 10w-30 can handle high temperatures well.
- Long-Term: Provides consistent protection and potentially extends engine life due to better performance across temperature ranges.
Now that I’ve gone over the key differences, let’s go into more detail about each oil. But, to keep it short: if you’re in a location that has large temperature fluctuations, shoot for the 10w-30, whereas if you live somewhere that is warmer and the temperature doesn’t fluctuate much, go for the SAE 30.
SAE 30
SAE 30 oil is a single-grade motor oil characterized by its stable viscosity at a specific temperature. As a single-grade oil, SAE 30 does not change its thickness with varying temperatures, maintaining a consistent performance level in warmer conditions. This type of oil is often recommended for use in older engines and specific types of machinery that operate under steady temperature conditions.
| Pros | Cons |
|
|
Key Characteristics and Features
- Stable Viscosity: SAE 30 oil maintains a consistent thickness and flow rate at operating temperatures, typically around 100°C (212°F). This stability makes it reliable for engines that do not experience wide temperature fluctuations.
- Simplicity: The straightforward formulation of SAE 30 oil makes it an excellent choice for older engines that were originally designed to use single-grade oils. This simplicity often translates to a lower cost compared to multi-grade oils.
- Lubrication Efficiency: Despite being a single-grade oil, SAE 30 provides effective lubrication, reducing friction and wear within the engine, thus helping to prolong the engine’s lifespan.
Benefits of Using SAE 30 over 10w-30
For individuals engaged in off-grid living or DIY projects, SAE 30 oil offers several significant advantages:
- Cost-Effectiveness: Given its simpler formulation, SAE 30 oil is often more affordable than multi-grade oils, making it a cost-effective choice for maintaining multiple pieces of equipment.
- Reliability: In warmer climates, where temperatures do not fluctuate drastically, SAE 30 oil provides reliable performance. This reliability ensures that engines and machinery run smoothly, reducing the likelihood of unexpected breakdowns.
- Compatibility: SAE 30 is compatible with a wide range of older engines, making it a versatile option for various types of off-grid machinery. This compatibility ensures that older, yet still functional, equipment remains in good working order.
In summary, SAE 30 oil is a practical and efficient choice for those maintaining engines and machinery in warm, stable climates. Its stable viscosity, cost-effectiveness, and compatibility with older engines make it a a great choice. By choosing SAE 30 for appropriate applications, you can ensure that your equipment runs reliably and efficiently, while also saving some cash.
10w-30
10w-30 oil is a versatile multi-grade motor oil designed to provide reliable performance across a wide range of temperatures. Unlike single-grade oils, 10w-30 adjusts its viscosity to suit different temperature conditions, making it a popular choice for many types of engines and machinery. This adaptability is particularly beneficial for those living in areas with large fluctuations in temperature, where equipment may be used in varied and sometimes harsh environments.
| Pros | Cons |
|
|
Key Characteristics and Features
- Multi-Grade Viscosity: The “10w” in 10w-30 indicates its viscosity at low temperatures (the “w” stands for winter), ensuring easier engine starts in cold conditions. The “30” denotes its viscosity at the engine’s operating temperature, providing consistent lubrication and protection.
- Temperature Adaptability: 10w-30 oil is formulated to perform well in both cold and warm temperatures, making it suitable for environments with varying weather conditions. This adaptability helps maintain engine performance and longevity regardless of the season.
- Enhanced Protection: The formulation of 10w-30 often includes additives that provide enhanced protection against wear, corrosion, and sludge build-up, which is essential for keeping engines in top condition over extended periods.
Benefits of Using 10w-30 over SAE 30
10w-30 oil offers several significant benefits for those involved in off-grid living and DIY projects:
- Versatility: The ability of 10w-30 to perform well in a wide range of temperatures makes it a versatile choice for many types of equipment. This versatility is especially valuable for off-grid living, where weather conditions can be unpredictable.
- Ease of Use: With its multi-grade properties, 10w-30 oil simplifies maintenance routines. Users don’t need to switch oils seasonally, reducing the complexity of engine care.
- Engine Protection: The advanced additives in 10w-30 oil help protect engines from wear and tear, extending the life of critical equipment.
- Fuel Efficiency: By maintaining proper lubrication and reducing engine friction, 10w-30 oil can help improve fuel efficiency. This is a significant advantage for off-grid living, where fuel resources may be limited.
In conclusion, 10w-30 oil is an excellent choice for those maintaining engines and machinery in challenging conditions. Its multi-grade viscosity, enhanced protection, and versatility make it a great choice for those who live where temperatures fluctuate a lot.
What to Choose: SAE 30 vs. 10w-30
Choosing between SAE 30 and 10w-30 oil will come down to the specific needs of your equipment and the environment in which you operate. Below are the key factors to consider when making this decision, along with guidance on when each type of oil is most advantageous.
Key Factors to Consider
- Climate and Temperature Range:
- SAE 30: Best suited for warm climates with stable temperatures. It provides consistent performance in high-temperature conditions but is not suitable for cold weather.
- 10w-30: Ideal for environments with varying temperatures, offering reliable performance in both cold and warm conditions. The multi-grade nature ensures easy starts in cold weather and consistent lubrication at operating temperatures.
- Type of Equipment:
- SAE 30: Recommended for older engines and equipment designed for single-grade oils. Commonly used in lawn mowers, small tractors, and certain garden machinery.
- 10w-30: Suitable for a wide range of modern engines and versatile enough for use in generators, vehicles, and other power tools. It’s the go-to choice for equipment that operates year-round in different weather conditions.
- Engine Age and Design:
- SAE 30: Preferred for older engines that were originally designed to run on single-grade oils. These engines benefit from the stable viscosity of SAE 30.
- 10w-30: Better suited for newer engines that are engineered to take advantage of multi-grade oil technology, providing better protection and performance.
- Usage Patterns:
- SAE 30: Excellent for equipment used primarily in warmer months or consistently warm climates. It’s simple and often more cost-effective for seasonal use.
- 10w-30: Best for equipment used throughout the year or in climates with significant temperature changes. Its versatility makes it a practical choice for continuous or varied use.
When to Choose SAE 30
SAE 30 is more favorable in the following situations:
- Consistent Warm Climates: If you live in an area where temperatures remain warm throughout the year, SAE 30 oil provides reliable performance without the need for the adaptability of a multi-grade oil.
- Older Engines: For older engines or those specifically designed for single-grade oils, SAE 30 offers the stability and simplicity these engines require.
- Specific Equipment: Ideal for lawn mowers, small tractors, and garden machinery that are typically used in warm weather conditions.
- Cost-Effectiveness: If cost is a significant factor and the equipment operates in a stable temperature environment, SAE 30 can be a more economical choice.
When to Choose 10w-30
10w-30 is preferable in the following situations:
- Varying Temperatures: If your equipment needs to operate in a climate with significant temperature fluctuations, 10w-30 ensures reliable performance and protection across a wide range of conditions.
- Year-Round Use: For equipment that is used throughout the year, including in cold weather, 10w-30’s adaptability makes it a versatile choice.
- Modern Engines: Engines designed for multi-grade oils benefit from the advanced formulation of 10w-30, which provides better protection and efficiency.
- Versatile Applications: Suitable for generators, vehicles, power tools, and other equipment that need to perform reliably in both cold and warm weather.
Additional Tips for Choosing
To make an informed decision:
- Check the Manufacturer’s Recommendations: Always refer to the equipment’s manual for the recommended oil type. This ensures compatibility and optimal performance.
- Assess Your Environment: Consider the typical temperatures and climate conditions in your area. Choose SAE 30 for warm, stable climates and 10w-30 for regions with varying temperatures.
- Evaluate Your Equipment Usage: Think about how and when you use your equipment. For seasonal use in warm weather, SAE 30 is suitable. For year-round or diverse usage, 10w-30 is the better choice.
By considering these factors, you can select the right oil to ensure your equipment runs smoothly, efficiently, and reliably, no matter the conditions.
In Closing
Choosing between SAE 30 and 10w-30 oil is a crucial decision that can significantly impact the performance and longevity of your equipment.
Recap of Main Points:
- SAE 30 is a single-grade oil with stable viscosity, ideal for older engines and equipment operating in consistently warm climates.
- 10w-30 is a multi-grade oil that adapts to varying temperatures, providing reliable performance in both cold and warm conditions, making it suitable for modern engines and year-round use.
Importance of Choosing the Right Oil: Selecting the correct oil type ensures that your equipment runs smoothly and efficiently. Using SAE 30 in the appropriate conditions prevents issues related to cold starts and insufficient lubrication, while 10w-30’s versatility protects engines in diverse environments. The right choice minimizes wear and tear, extends engine life, and enhances overall reliability.
By considering these factors, you can make an informed decision that ensures your machinery operates reliably and efficiently, allowing you to keep your equipment in top condition and ready for any project or challenge that comes your way.
Additional Resources and Data Sources
Here are some links to additional resources as well as some references from within the article.
- Information on Operating Temps of different Oils
- Valvoline 10w-30 Information
- Oil Viscosity Explained
If you have any more questions about SAE 30 vs 10w-30, feel free to reach out to me any time.
God Bless!




